

关注微信公众号

前往手机站

盲肠结扎穿孔以及电针刺激


酶联生物经过不断的实验优化和改进,积累了大量的经验,拥有专业的酶联研发团队。利用专业的酶联免疫技术自主研发的elisa试剂盒,能对血清及其它样本定量检测抗原,定性检测特异性抗体。优质的试剂,先进的仪器和正确的操作是保证ELISA检测结果准确可靠的必要条件。ELISA检测的方便性、稳定性、重复性和可靠性方面都具有很大的优势。
ELISA检测技术服务内容:
1、双抗体夹心法检测抗原 2、间接法检测抗体 3、为客户提供各种ELISA技术进行样本检测。
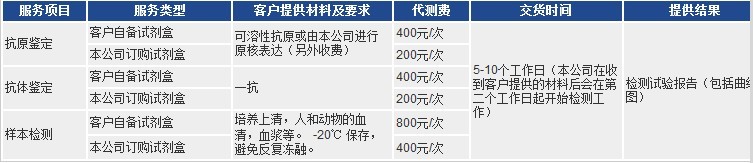
以上代测费,凡购买本公司试剂盒,我们免费代测!
凡购买本公司目录任何一种酶联免疫检测试剂盒,您只需将需要检测的动物(Human, Rat, Mouse, Rabbit, Monkey,
Pig……)种类和检测指标(白介素类、激素类)及标本数量(48T/96T)通知公司业务员即可。在接到客户标本当日起,现货产品一周内将检测报告交到客户手中!
欢迎各科研单位在各种项目上与我们公司开展不同层次的密切合作,以双赢求发展,共同进步,为中国检测事业的发展积累经验。
二、样本要求
在收集标本前都必须有一个完整的计划,必须清楚要检测的成份是否足够稳定。我们提倡新鲜标本尽早检测,对收集后当天就进行检测的标本,及时储存在4℃备用,如有特殊原因需要周期收集标本,请造模取材后,将标本及时分装后放在-20℃或-70℃条件下保存。因冰室与室温存在一定温差,蛋白极易降解,直接影响实验质量,所以避免反复冻融。代测放免标本的客户取材前须向我司销售人员索要说明书,具体操作注意事项请与我司技术人员沟通。
液体类标本:标本必须为液体,不含沉淀。包括血清、血浆、尿液、胸腹水、脑脊液、细胞培养上清、组织匀浆等。
血清:室温血液自然凝固10-20分钟后,离心20分钟左右(2000-3000转/分)。收集上清。如有沉淀形成,应再次离心。
血浆:应根据试剂盒的要求选择EDTA、柠檬酸钠或肝素作为抗凝剂,加入10%(v/v)抗凝剂(0.1M柠檬酸钠或1%heparin 或2.0%EDTA.Na2)混合10-20分钟后,离心20分钟左右(2000-3000转/分)。仔细收集上清。如有沉淀形成,应再次离心。
尿液、胸腹水、脑脊液:用无菌管收集。离心20分钟左右(2000-3000转/分)。仔细收集上清。如有沉淀形成,应再次离心。
细胞培养上清:检测分泌性的成份时,用无菌管收集。离心20分钟左右(2000-3000转/分)。仔细收集上清。检测细胞内的成份时,用PBS(PH7.0-7.4)稀释细胞悬液,细胞浓度达到100万/ml左右。通过反复冻融,以使细胞破坏并放出细胞内成份。离心20分钟左右(2000-3000转/分)。仔细收集上清。保存过程中如有沉淀形成,应再次离心。
组织标本:切割标本后,称取重量。加入一定量的PBS,缓冲液中可加入1μg/L蛋白酶抑制剂或50U/ml的Aprotinin(抑肽酶)。用手工或匀浆器将标本匀浆充分。离心20分钟左右(2000-3000转/分)。仔细收集上清置于-20度或-70度保存,如有必要,可以将样品浓缩干燥。分装后一份待检测,其余冷冻备用。
三、寄标本时需注明以下情况:
1、标本编号;2、所测项目;3、是否做复孔;3、联系方式;4、实验后标本是否寄回。
客户须知:
客户应对所提供的材料及信息负责,如因客户提供的材料及信息不准确而引起的实验延误或经济损失由客户承担。
Q:1.
how to collect samples and preparation of ELISA?
Performed by ELISA test is generally common clinical samples including blood (finger
blood, blood), urine, feces, cerebrospinal fluid, pleural effusion, prostatic fluid,
semen, vaginal secretions, which
Some time of sample collection, preservation methods and has certain requirements.
Collection (a) clinical specimens
A, blood samples:Some physiological factors, such as smoking, eating, exercise, mood
swings, pregnancy, postural changes in blood can affect certain ingredients, even some
of diurnal variation. Therefore, blood samples
Acquisition should avoid interference physiological factors, consistent with appropriate
conditions, such as can not be avoided, should indicate the factors on the specimen.
1. Peripheral:Usually select the inside of blood left ring finger, the portion should be
no frostbite, inflammation, edema, damage. If the site does not meet the requirements to
other parts of the fingers instead. For burn patients, optional leather
Intact skin at the blood. As part of routine blood tests (eg, white blood cell count,
sort, etc.) affected by physiological factors fluctuation is too large, when compared to
the conditional should be consistent. It relates to the body, blood clotting function
Can test items (such as platelet count, bleeding time or clotting time) testing, we must
pay attention to understand whether the patient used anticoagulant, procoagulant drugs
in order to reduce or avoid interfering factors
influences.
2. Blood:In addition to involving a variety of projects such as hemostasis and
thrombosis detector requires the use of anticoagulated blood plasma, the current
analysis to detect the vast majority of projects can be directly detected using blood
serum. In the serum test items
, Some (such as blood sugar, blood fat) diet and circadian factors influenced, fasting
blood samples were generally appropriate; some decay rapidly in the blood (serum enzyme
activity assay such as ACP activity, etc.),
0 ~ 4 ℃ storage is not an activity decreased, the detection of these projects must be
timely and fast; some (such as creatine kinase) influenced by exercise and other
factors. Avoid hemolysis occurs when blood is also important
And, more particularly potassium, LDH and other measurement.
B, urine samples:With the same blood samples, urine samples affect diet, exercise,
medication and other factors that are also large, especially on the diet, so the morning
urine generally superior to random urine. Means getting up early morning urine
After the first urine specimens, representing concentrated and acidified visible
components (such as blood cells, epithelial cells, tubular) easy to observe the relative
concentration. Random urine that is a random urine specimens convenient, but by diet,
Sports, and even more the influence of drugs, prone to false positive and false negative
results, such as diet proteinuria, glucosuria diet, vitamin C interference occult blood
results and the like. Postprandial urine (patient 2 hours after lunch, collected
Human Urine) suitable for urine, urine protein and urobilinogen check urine samples at
this time to increase the sensitivity of the test, the detection of minor lesions. 12
hours in urine cell count is Addis count (last night 8:00
After emptying the bladder to all specimens of urine 8 o'clock the next morning),
because a long time, easy to breed bacteria shall be added preservative formaldehyde.
24-hour urine (the first day of the morning after emptying the bladder specimens from
8:00 to 8:00 the next morning
All urine) quantification of chemical substances, including proteins, sugars, urinary
17-one, 17-hydroxy steroids, catecholamines, Ca2 +, etc., to detect different
substances, choose a different preservative preservative. clean
Urine used for urine bacterial culture requires sterile specimens were taken after
washing the vulva. Urine specimens should be enough to collect all, at least 12 ml,
preferably 50 ml, the timing must collect all the urine of women
Patients should avoid vaginal secretions, blood contamination of urine specimens.
C, stool samples:Stool samples for the detection judgment digestive diseases has
important reference value. Collection requirements with a clean bamboo select faecal
mucus, pus and blood components and other abnormality, no abnormal appearance
Droppings shall be drawn from multiple surface and deep manure end. Get parasitemia and
for egg counts should be collected 24 hours feces. Dysentery amoeba trophozoites check
should immediately check in after a bowel movement, and from there sepsis
Softer at the drawn, insulation inspection. Charles S. japonicum eggs should take mucus,
pus and blood portion 30g stool specimens from at least miracidia hatching, and to be
treated as soon as possible. Check pinworm eggs must use transparent film swab
Night before 12:00 or early in the morning from defecation wrinkled folds around the
anus and immediately swabbing at microscopic examination. Occult blood test (chemistry),
fasting before the test on the 3rd of meat and foods containing animal blood and ban
clothing iron, vitamin C and so on.
Should be checked in all 1 hour stool specimen collection is completed, in order to
prevent damage to physical components of digestive enzymes and pH by. For clinical
samples above the detection indicators.
D, CSF samples:CSF samples collected immediately after submission, place too long will
affect the test results: such as cell degeneration, destruction, leading to counting and
classification are not allowed; some chemicals such as glucose content will decompose
Save
Less; bacteria occur autolysis affect bacteria detection rate. Cerebrospinal fluid
extracted three general dispensing a sterile tube, the first tube for bacterial culture,
a second tube for chemical analysis and immunological tests, the third tube for general
Characters and microscopic examination, three of the order should be reversed. Specimen
collection is difficult because all inspection and testing process should pay attention
to safety.
E, ascites and pleural effusion samples:CSF samples with the same attention to safety
after the specimen collection, and timely submission. Generally separated into three
tubes, one for routine cytology, a biochemical examination, a bacterial culture, in
order
CSF same is appropriate.
F, prostatic fluid sample:Prostatic fluid specimen after prostate massage by the
acquisition, directly drop when less liquid on a glass slide and timely submission shall
be taken to prevent sample evaporation to dryness, the amount collected for a long time
in a clean, dry test tube. If massage
No prostatic fluid, urine sediment can be checked after the massage.
G, semen samples:Abstinence before semen collection should be 3 to 7 days, drain the
urine after masturbation or other available methods of semen directly into clean
containers, insulation and timely submission. Due to changes in sperm production during
the day and
Large, generally should be checked 2 to 3 times (each time interval of 1 to 2 weeks) in
order to make a diagnosis.
H, samples of vaginal secretions:Vaginal samples were collected 24 hours before
intercourse should be prohibited, bath, vaginal examination, vaginal lavage and local on
the drug, etc., drawing instruments used need to be cleaned. Usually with brine-soaked
cotton swab from the vagina deep
Or rear vaginal fornix, cervical canal mouth drawn, etc., made after saline smear
vaginal secretion samples observation, women with menstrual vaginal secretions were not
checking.
2, do before each sample by ELISA experiment how to prepare?
Before collecting the sample must have a comprehensive plan must clearly be detected
component is stable enough. To be collected on the same day
Sample testing, and timely backup stored at 4 ℃. For the next day re-testing samples
frozen in a timely manner after dispensing -20 ℃ spare, conditional, preferably -70 ℃
cryopreservation standby. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing specimens
.
Liquid samples: including serum, plasma, urine, pleural effusion, cerebrospinal fluid,
cell culture supernatant and the like.
1. serum:
Coagulation at room temperature 10-20 mins, centrifugation 20 minutes or so (2000-3000
rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant. If precipitation during storage,
Centrifugal again.
2. Plasma:
EDTA should be selected according to the requirements of the specimen, sodium citrate or
heparin as an anticoagulant, mix 10-20 mins, centrifugation 20 minutes or so (2000-3000
rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant. Save process
If precipitation appeared, Centrifugal again.
3. Urine:
Sterile collection tube. Centrifuged for 20 minutes or so (2000-3000 rev / min).
Carefully collect the supernatant. If precipitation during storage, Centrifugal again.
Pleural and peritoneal effusions, and cerebrospinal fluid Reference to this practice.
4. The cell culture supernatant:
The detection of secretory component with a sterile collection tube. Centrifuged for 20
minutes or so (2000-3000 rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant.
5. cultured cells
????When the detection of intracellular components, diluted with PBS (PH7.2-7.4) cell
suspension, the cell concentration reached 1 million / ml or so. By repeated freezing
and thawing or tissue protein extraction reagent was added to the cells
Damage and release of intracellular components. Centrifuged for 20 minutes or so
(2000-3000 rev / min). Carefully collect the supernatant. If precipitation during
storage, Centrifugal again.
6. tissues